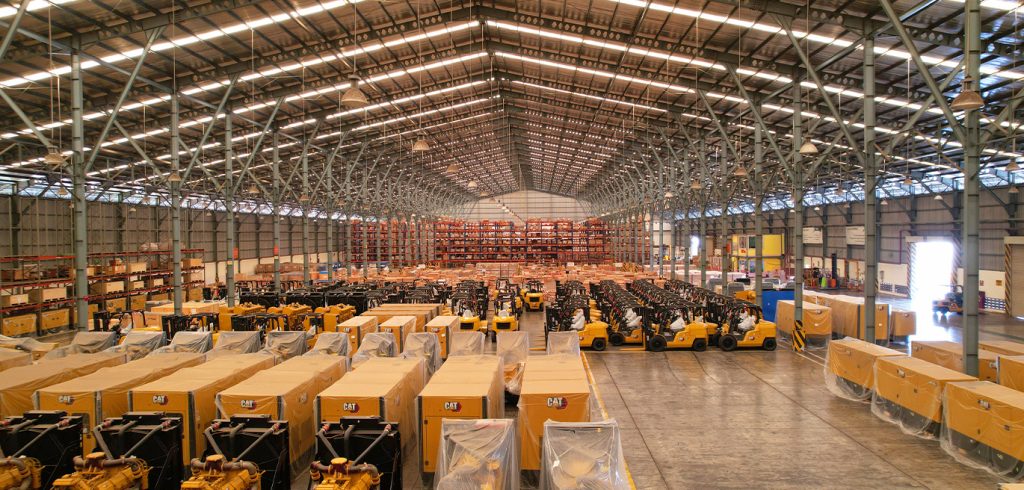
What is a Warehouse?
Definition and Purpose of a Warehouse
A warehouse is primarily defined as a large building designed for the storage of goods. It serves a crucial role in the supply chain, acting as an intermediary between the production and distribution phases of commerce. The primary purpose of a warehouse is to store products until they are needed, which enables businesses to manage inventory more efficiently and respond to market demands promptly. Whether used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, or transport companies, warehouses serve as essential hubs for logistics and distribution.
According to warehouse definitions found in industry literature, these facilities are typically large, plain structures located on the outskirts of urban areas and industrial parks, designed to facilitate the easy handling and storage of goods.
Types of Warehouses and Their Functions
Warehouses can be categorized into several types, each serving specific functions based on their operations and the needs of the businesses they support. Here are some of the most common types of warehouses:
- Public Warehouses: These are storage facilities available for rent by multiple businesses, providing flexibility for companies that do not want to commit to long-term storage.
- Private Warehouses: Owned and operated by a single company, these warehouses are tailored to a company’s specific needs and are often used by large retailers or manufacturers.
- Distribution Centers: Unlike traditional warehouses, distribution centers focus on the efficient distribution of goods rather than long-term storage. They are strategically located to enable faster shipping to customers.
- Climate-Controlled Warehouses: These facilities are essential for storing temperature-sensitive products, such as pharmaceuticals, food, and artwork, ensuring the integrity of these items.
- Container Storage: Primarily for international shipping, container storage warehouses are utilized to store cargo in shipping containers, making them ideal for companies involved in global trade.
Importance of Warehousing in Supply Chain Management
Warehousing plays a pivotal role in supply chain management, impacting several key areas:
- Inventory Management: Effective warehousing allows businesses to maintain optimal inventory levels, reducing holding costs and minimizing stockouts or overstock situations.
- Order Fulfillment: A well-organized warehouse streamlines the order fulfillment process, ensuring that products are readily available when needed and can be shipped quickly to customers.
- Cost Efficiency: By consolidating goods from multiple suppliers, warehouses can benefit from economies of scale, lowering shipping costs and enhancing profitability.
- Risk Mitigation: Warehousing helps businesses manage risks by storing enough products to meet unexpected demand fluctuations or supply chain disruptions.
Key Components of Warehouse Design
Storage Systems and Layout Planning
The layout of a warehouse is a critical component that influences its efficiency. Effective design maximizes space utilization and optimizes movement within the facility. Common strategies include:
- Vertical Storage: Utilizing vertical space with high racks helps increase storage capacity.
- Cross-Docking: This method involves receiving and shipping products simultaneously, reducing storage time.
- Modular Design: Crafting flexible storage solutions can adapt to changing inventory needs.
Implementing a strategic plan that considers the flow of goods, accessibility, and safety is essential for maximizing warehouse operations.
Essential Handling Equipment for Warehouses
Various equipment types are essential for efficient warehouse operations. These include:
- Forklifts: Used for lifting and transporting materials, forklifts are vital for handling heavy or bulky items.
- Pallet Jacks: Smaller and more maneuverable, pallet jacks assist in moving pallets of goods.
- Conveyors: Automating the movement of goods within the warehouse, conveyors save time and labor costs.
- Storage Racks and Shelving Units: These vary in style and storage capacity, designed to streamline product retrieval.
Investing in the right handling equipment enhances operational efficiency and workplace safety.
Safety Measures and Compliance Standards
Safety in the warehouse is paramount. Compliance with industry standards and regulations ensures employee safety and minimizes liability. Key measures include:
- Employee Training: Regular training on safety protocols and equipment operation helps prevent accidents.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Ensuring employees are equipped with PPE, such as gloves, helmets, and safety shoes, reduces injury risk.
- Regular Inspections: Conducting routine safety audits and equipment checks helps identify potential hazards and maintain compliance.
- Emergency Preparedness Plans: Being prepared with emergency procedures ensures quick responses to accidents or natural disasters.
Warehouse Management Best Practices
Inventory Control Techniques
Effective inventory control is crucial for warehouse management. Techniques that can enhance accuracy and efficiency include:
- ABC Analysis: Classifying products based on their importance allows warehouses to focus resources on high-value items.
- Just-in-Time (JIT) Inventory: This strategy encourages businesses to keep minimal stock and rely on timely supplier deliveries.
- Real-Time Inventory Tracking: Using barcodes or RFID technology enhances visibility and accuracy in inventory management.
Utilizing Technology in Warehouse Management
Technology plays a transformative role in warehouse management. Key innovations include:
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Software designed to streamline warehouse operations, including inventory tracking, order processing, and labor management.
- Automation: Using robotic systems to pack, pick, and ship products can greatly enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs.
- Data Analytics: Leveraging data for forecasting and performance monitoring allows warehouses to adapt dynamically to market changes.
Workforce Optimization and Training Strategies
Optimizing workforce performance is vital for warehouse productivity. Key strategies include:
- Labor Management Systems: Implementing systems to track employee productivity helps identify areas for improvement and adjust staffing levels accordingly.
- Ongoing Training: Regular skills training keeps workers informed about new technologies and safety practices, enhancing efficiency.
- Incentive Programs: Offering performance incentives encourages employees to meet and exceed productivity goals.
Common Challenges in Warehouse Operations
Addressing Space Constraints and Scalability
As businesses grow, space constraints become a significant challenge. Strategies to overcome these include:
- Vertical Expansion: Investing in high stacking systems maximizes available space.
- Flexible Space Design: Creating multifunctional areas can accommodate varying inventory levels and types.
- Outsourcing Storage Solutions: Utilizing third-party logistics providers can alleviate strain on a company’s primary warehousing operations.
Managing Labor Costs and Productivity
Labor costs are a significant portion of warehouse expenses. Effective management strategies include:
- Efficient Scheduling: Utilizing scheduling software can optimize workforce deployment and reduce overtime costs.
- Performance Monitoring: Regular review of employee performance metrics helps identify productivity bottlenecks and develop improvement plans.
- Team Collaboration: Fostering a collaborative environment encourages employees to work more effectively together, improving overall productivity.
Overcoming Logistical Hurdles in Warehousing
Logistics play a fundamental role in warehousing. Common challenges include:
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Building strong relationships with multiple suppliers can help mitigate the impact of unexpected shortages.
- Transportation Coordination: Integrating transportation management can streamline goods movement, minimizing delays.
- Inventory Inaccuracy: Emphasizing precise tracking and regular auditing can maintain inventory integrity and reliability.
Future Trends in Warehousing
The Impact of E-commerce on Warehouse Operations
The explosion of e-commerce has dramatically reshaped warehousing, driving innovations like:
- Fulfilling Rapid Orders: Warehouses need to adapt to increasingly high customer expectations for fast deliveries, necessitating more efficient operations.
- Returns Management: The rise in online returns demands that warehouses develop robust processes for handling returned goods.
- Omnichannel Strategies: Warehouses are integrating processes that support both online and physical store inventories, providing a seamless shopping experience.
Sustainability in Warehouse Management
As environmental concerns rise, sustainability is becoming an essential focus in warehouse management. Strategies include:
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems reduces operational costs and environmental impact.
- Waste Reduction: Employing recycling programs and minimizing packaging materials contribute to sustainable practices.
- Green Certifications: Pursuing certifications like LEED can enhance a warehouse’s reputation and attract eco-conscious clients.
Emerging Technologies Transforming Warehousing
Technological advancements continue to transform the warehousing landscape. Notable innovations include:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-driven analytics improve demand forecasting and inventory optimization.
- Blockchain: This technology ensures transparency and traceability in supply chains, enhancing trust among stakeholders.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices enable real-time monitoring of inventory and equipment performance, aiding in preventive maintenance.