Understanding Structural Steel Welding
What is Structural Steel Welding?
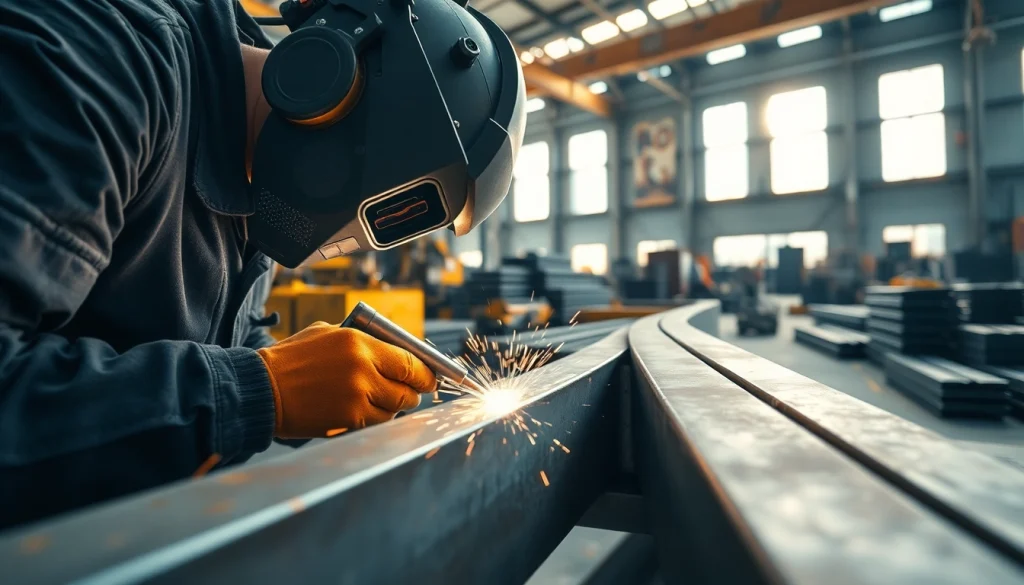
Structural steel welding is the technical process of joining metal components, specifically steel, to create a cohesive whole that serves various engineering and construction purposes. It involves a systematic approach where welded joints are created to ensure strength, durability, and the capability to withstand the physical stresses expected in its intended application. This foundational technique is integral in crafting buildings, bridges, and numerous other infrastructure elements. If you’re looking to learn more about structural steel welding, the techniques and equipment required can vary significantly depending on the project specifications.
Importance in Construction and Engineering
The significance of structural steel welding in construction and engineering cannot be overstated. As a crucial component, it enhances the structural integrity of buildings and other constructions. Welded joints resist tensile and compressive forces, which are vital for the stability of structures that experience varying loads and stresses. Moreover, structural steel welding facilitates the rapid assembly of components on-site, which contributes to efficient construction timelines. Therefore, understanding the methods and best practices surrounding structural steel welding is essential for ensuring the successful execution of structural designs.
Key Materials Used in Structural Steel Welding
Welding typically involves various materials, with structural steel being the predominant type used. Various grades are selected based on the requirements of a project, such as tensile strength and hardness. Common materials also include alloyed steels, which add enhanced properties to the base steel, and filler metals that complement the parent material during the welding process. The choice of materials directly influences the welding process and the overall quality of the weld, making it essential to select appropriately for specific applications.
Common Methods of Structural Steel Welding
MIG and TIG Welding Techniques
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) and TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding are two prevalent techniques commonly utilized in structural steel welding. MIG welding is favored for its speed and ease of use; it employs a continuous wire feed as the electrode and an inert gas to shield the weld pool, ensuring that the weld remains clean and robust. On the other hand, TIG welding utilizes a non-consumable tungsten electrode, allowing greater control over the weld and producing high-quality, intricate welds, especially for thinner materials. Both methods have their unique advantages and are chosen based on project specifications and desired outcomes.
Stick Welding Applications
Stick welding, also known as Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), is another popular method for structural steel welding, especially in outdoor environments or where portability is essential. This technique involves using an electrode coated with flux that melts during the process to protect the weld area from contamination. Stick welding is particularly advantageous in situations that require versatility because it can be performed in all positions, making it suitable for a wide range of industrial and construction applications.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Project
The selection of a welding method depends on various factors, including the type of steel being used, joint configuration, position, and environmental conditions. Projects requiring minimal penetration and high precision may benefit more from TIG welding, while larger and thicker components can utilize MIG or stick welding methods for their efficiency and strength. Understanding these nuances is vital for achieving the desired structural integrity and performance of welded joints in construction.
Challenges in Structural Steel Welding
Identifying Common Welding Defects
Structural steel welding is not without its challenges. Common welding defects such as cracks, porosity, undercutting, and lack of fusion can jeopardize the integrity of a welded joint. These defects can arise due to various factors, such as incorrect settings, improper material selection, or inadequate preparation of the workpieces. Recognizing these potential flaws early in the process is crucial, as it allows welders to implement corrective measures before finalizing the weld.
Mitigation Strategies for Welding Issues
To mitigate issues that may arise during structural steel welding, welders should develop a robust strategy that includes thorough preparation of materials, proper selection of the welding technique, and consistent monitoring of the welding process. Using preheating techniques for certain metals can help reduce the risk of cracking. Additionally, routine inspection and testing of the welds can identify defects, allowing for timely repairs or adjustments to ensure compliance with structural standards.
The Impact of Environment on Welding Quality
Environmental conditions can significantly affect the quality of welds. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind exposure can lead to defects like warping or inadequate fusion. When welding in less than ideal conditions, it’s essential to implement protective measures, such as wind barriers or the use of temporary shelters, to maintain consistent temperatures and shielding of the weld from contaminants. Adapting the welding technique based on environmental conditions can enhance the effectiveness of the weld.
Safety Measures in Structural Steel Welding
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Safety is paramount in structural steel welding. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is a critical element in safeguarding welders from various hazards. Essential PPE includes welding helmets equipped with appropriate lenses to protect against harmful UV and IR radiation, gloves designed to withstand high temperatures, and flame-resistant clothing to prevent burns and injuries. Ensuring that all workers are properly equipped with the necessary protective gear contributes to a reduced risk of accidents and injuries on site.
Best Practices for Safe Welding Operations
Adopting best practices for welding operations can further mitigate risks. This includes maintaining a clean work environment to prevent slips, trips, and falls, conducting regular safety training sessions for staff, and ensuring that all equipment adheres to safety standards. Welders should always remain vigilant and have a well-constructed plan in place for handling both routine and emergency situations. Engaging in clear communication among team members can also enhance safety outcomes.
Emergency Procedures and First Aid
Establishing emergency procedures is essential for addressing accidents should they occur during structural steel welding. Workers must be trained in first aid practices, focusing on how to treat burns, eye injuries, and electrical shocks that may arise from welding operations. Regular practice of emergency protocols, including evacuation routes and communication hierarchies, can help ensure a rapid and effective response in case of an accident, ultimately saving lives and minimizing injuries.
Future Trends in Structural Steel Welding
Technological Advancements in Welding Equipment
The future of structural steel welding is increasingly shaped by technological advancements. Innovations in automation and robotics are enhancing the efficiency and precision of welding. Equipment incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning is being developed to predict equipment failures, offering predictive maintenance options that can significantly reduce downtime. Furthermore, improvements in welding technology are positively impacting overall safety and effectiveness in steel fabrication.
Sustainability Practices in Welding
As industries become more environmentally conscious, sustainability practices in structural steel welding are gaining prominence. This includes adopting eco-friendly welding processes and materials, reducing welding fumes, and recycling scrap materials generated during welding operations. The shift towards sustainable welding not only reduces the environmental footprint but also aligns with growing regulatory requirements for sustainability in construction.
Training and Skill Development for Welders
The need for continuous training and skill development among welders is vital as techniques evolve. On-going education programs can significantly enhance a worker’s ability to adapt to new technologies and methods, ensuring they remain competitive within the industry. Certification programs and workshops focused on the latest advancements in welding technology are also essential for maintaining high standards of safety and quality in the sector.
Frequently Asked Questions
What type of welding is used for structural steel?
The most common welding methods for structural steel include MIG, TIG, and Stick welding. Each method has unique advantages suited to different applications.
What does a structural steel welder do?
A structural steel welder is responsible for joining steel components to construct buildings, bridges, and other infrastructures, ensuring the structures’ integrity and stability.
Is structural welding a good career?
Yes, structural welding offers strong job security and competitive salaries as the demand for skilled welders remains high in many industries, especially construction and manufacturing.
Which is better, SMAW or GMAW?
Both SMAW and GMAW have their pros and cons, with the right choice depending on the project requirements. SMAW excels in ruggedness, while GMAW offers cleaner and faster results.
What are common defects in structural welding?
Common defects include cracks, porosity, lack of fusion, and undercutting. Proper technique and preparation of materials can help minimize these issues.